Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
zymtrace uses Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to manage user permissions. Roles are assigned to users, and each role contains a set of permission patterns that define what actions the user can perform.
Assign built-in roles to users via Profile picture → Account → Users → select user → Edit → add roles → Save
How RBAC Works
- Roles are assigned to one or more users
- Roles contain permission patterns (not individual permissions)
- Permission patterns use wildcards to match multiple permissions
- Services validate requests by matching required permissions against patterns in the token
Permission Patterns
Permission patterns use a hierarchical format with wildcard support:
resource:subresource:action
Wildcard Types:
*- matches a single level (e.g.,project:*matchesproject:create,project:read)**- matches multiple levels (e.g.,**:readmatchesproject:read,admin:user:read, etc.)
Examples:
# Allow all project operations
project:*
# Allow reading anything
**:read
# Allow all admin operations
admin:**
# Allow all service token operations
service:token:*
# Allow everything (admin role)
**:**
Built-in Roles
zymtrace includes three default roles:
System Admin(full system access with all permissions)System Editor(can edit all system resources)System Viewer(read-only access to all system resources)Default Project Viewer(all users have read-only access to the default project)
Permission Model
Understanding available permissions is essential for creating custom roles.
Service Token Permissions
| Description | Permission |
|---|---|
| Create service tokens | service:token:create |
| View service tokens | service:token:read |
| Revoke service tokens | service:token:revoke |
Project Permissions
| Description | Permission |
|---|---|
| Create new projects | project:create |
| View project details | project:read |
| Modify project settings | project:update |
| Delete projects | project:delete |
Admin User Permissions
| Description | Permission |
|---|---|
| Create user accounts | admin:user:create |
| View user accounts | admin:user:read |
| Modify user accounts | admin:user:update |
| Delete user accounts | admin:user:delete |
Admin Role Permissions
| Description | Permission |
|---|---|
| Create custom roles | admin:role:create |
| View role definitions | admin:role:read |
| Modify role permissions | admin:role:update |
| Delete custom roles | admin:role:delete |
| Assign roles to users | admin:role:assignment:set |
Audit Permissions
| Description | Permission |
|---|---|
| View audit log entries | admin:audit:read |
Authentication Permissions
| Description | Permission |
|---|---|
| Log in with local credentials | auth:local:login |
Common RBAC Patterns
Here are practical role configurations for common use cases:
Read-Only Viewer
Perfect for stakeholders who need access but shouldn't make changes.
**:read
CI/CD Agent Role
For automated deployments and monitoring systems.
service:token:read
project:read
Project Manager
Can view and modify project settings, but cannot manage users or roles.
project:read
project:update
Analyst Role
Can create and view resources but cannot delete.
project:create
project:read
admin:audit:read
User roles can be managed in the admin page.
Managing User Roles
- Log in as an admin user
- Navigate to Profile picture → Account → Users
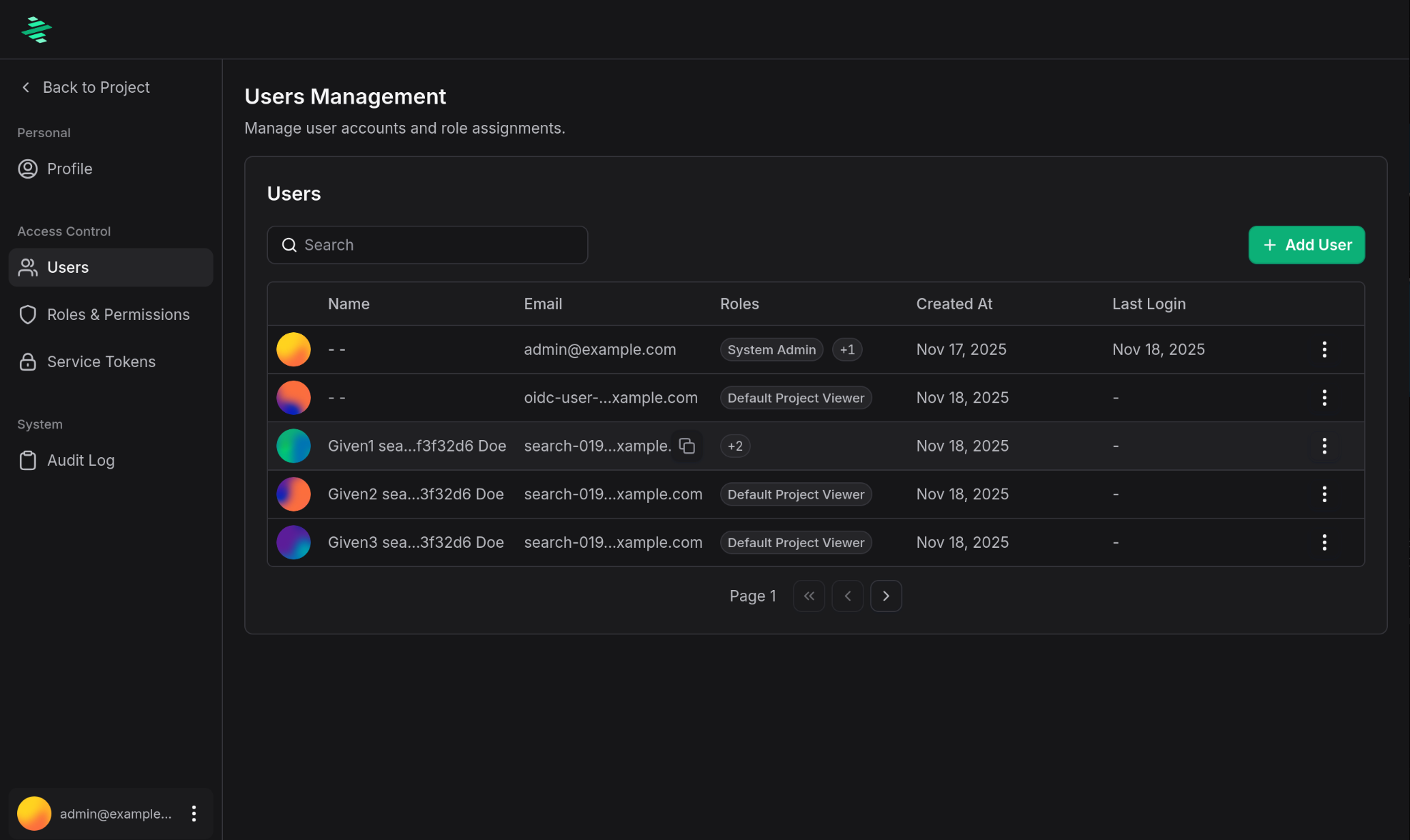
- Select a user and click three vertical dots
- Click Edit
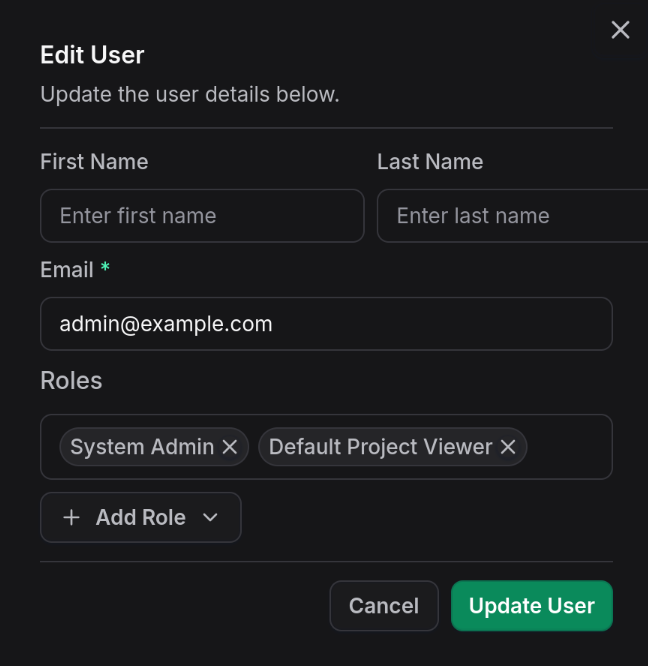
- Add or remove roles
- Save changes
Role changes apply when the user's next access token is issued. Access tokens are short-lived (typically 5 minutes), so changes take effect quickly.
Creating Custom Roles
Custom roles allow fine-grained access control tailored to your organization's needs.
- Navigate to Profile picture → Account → Users
- Click Role & Permissions
- Click Add Role
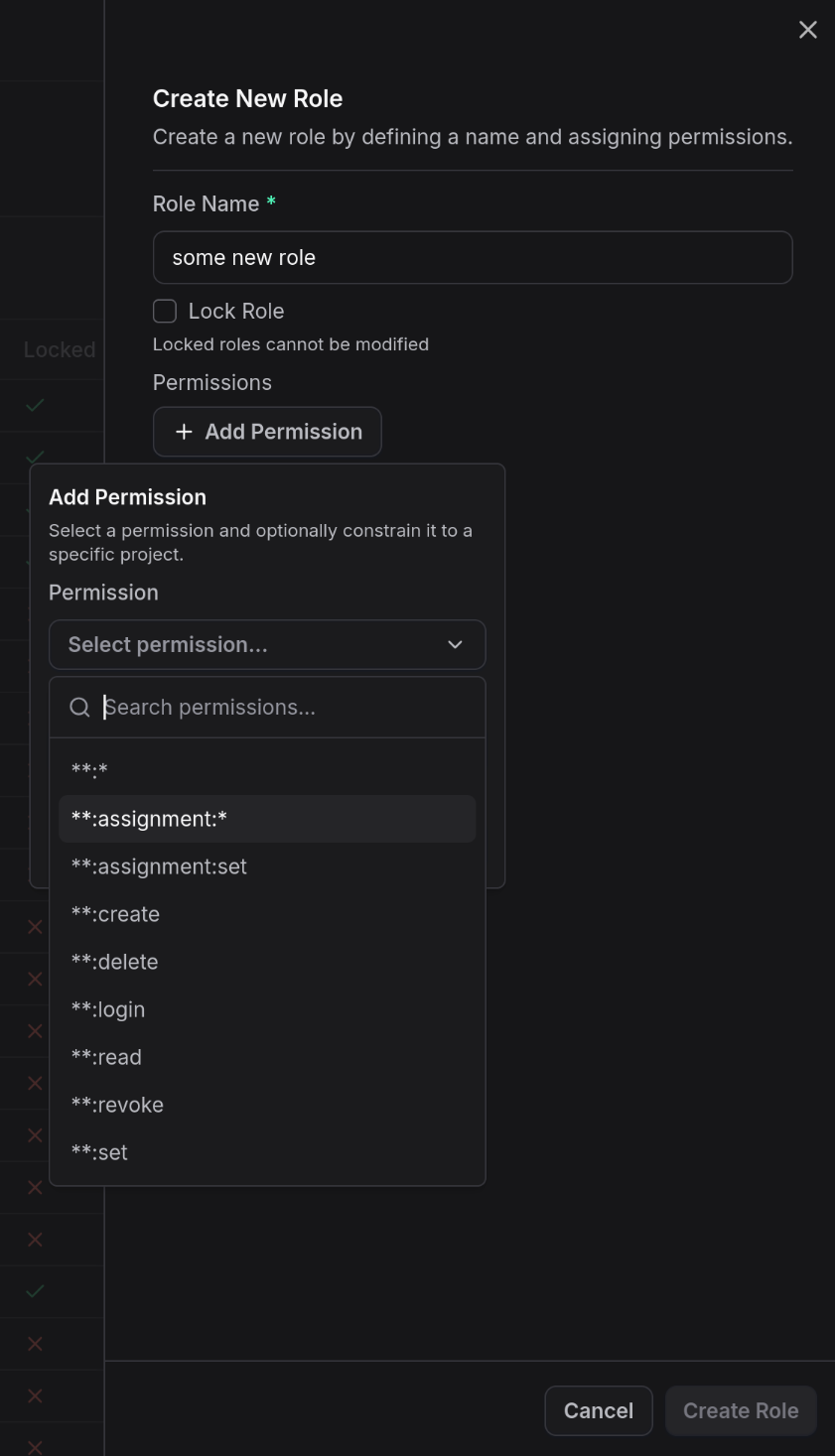
- Add permission patterns and role name
- Save the role
Roles with Constraints
Roles can be restricted to specific projects, enabling fine-grained project-level access control.
Project-Scoped Roles
When creating or editing a role, you can specify a list of projects the role grants access to:
- Navigate to Profile picture → Account → Users
- Click Role & Permissions
- Click Add Role or edit an existing role
- Add permission patterns
- Under Project Access, select which projects this role applies to
- Save the role
Example: Project Lead
A project-scoped role that allows users to manage a specific project:
project:read
project:update
Apply this role with project constraint to "Project A" to allow leadership to modify only that project's settings.
Audit Logging
All permission-related actions are logged to the audit log:
- Role assignments and removals
- Role creation, modification, and deletion
- Permission checks that result in denial
- Service token creation and revocation
- Admin actions on user accounts